About MICROFIL®
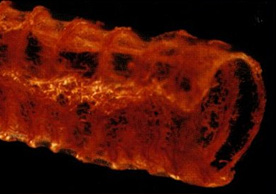
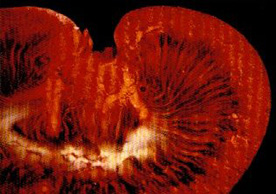
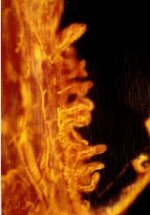
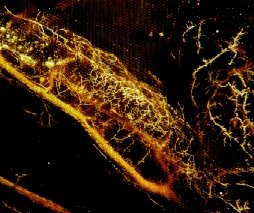
MICROFIL® compounds will fill and opacify microvascular and other spaces of non-surviving animals and post-mortem tissue under physiological injection pressure. The continuous, closed vascular system lends itself to flow through injection or perfusion techniques. Following injection, MICROFIL compounds cure to form a three-dimensional cast of the vasculature.
MICROFIL® MV-series compounds are available in five radiopaque colors, as well as clear. MV-series compounds require either an alcohol-methyl salicylate or glycerin clearing sequence, whereby the refractive index of the clearing solution is the same as the refractive index of the tissue. This allows for microscopic examination of a selected vascular bed.
Advantages offered with MICROFIL® compounds over previously available rubber injection materials include:
- Complete filling with minimal shrinkage, to enhance vessel continuity and to produce in cleared preparations a vivid, optically cleared specimen that allows a precise study of the microcirculation.
- Color diversity, to provide delineation within the circulatory tree for microscopic examination and photographic illustration.
Areas of Investigation
In physiology, MICROFIL® visualization provides a means for establishing the precise vascular architecture of specific organs, allowing comparison between normal and abnormal structure.
In surgery, visualization of the microcirculation and microanatomy is leading to improved surgical techniques in the repair of nerves, tendons, and blood vessels.
In gastrointestinal research, MICROFIL® compounds characterize and describe changes in vascular patterns associated with several pathological conditions.
Injected specimens, when preserved in methyl salicylate or glycerin, also serve as a definitive teaching adjunct.
MV-Series Mixing Procedure
To achieve a viscosity level suitable for injection of the microcirculation, it is necessary to blend the MV compound with an equal quantity (by weight) of MV-Diluent. Volume mixing requires 5ml of diluent for every 4ml of compound. The mixture of compound and diluent is catalyzed with 5% (by weight or volume) of MV Curing Agent. Viscosity ranges from 20 to 30 centipoise. Working time is 20 minutes and begins with the addition of curing agent.
Physical Properties of MICROFIL® Compound
| MV-112 | MV-117 | MV-120 | MV-122 | MV-130 | MV-132 | MV-Diluent | |
| Color | White | Orange | Blue | Yellow | Red | Clear | Clear |
| Specific gravity | 1.04 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 0.92 |
| Viscosity, centipoise | 35 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 30 | 20 | 5 |
| Gel time, minutes | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | - |
| Useful shelf life, months | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Indefinite |
Notes
- Viscosity measured with a Brookfield Model LVF Viscometer, with a No. 2 spindle at 30RPM.
- Gel time measured on a blend (by weight) of one part MV compound and one part MV-Diluent followed by addition of 5% MV Curing Agent. Gel time is time required for mixture to cease flowing.
- Shelf life is in excess of four months. For materials held beyond four months, it is possible to run the following static test to determine acceptability:
- Mix 5 grams of MV compound with 5 grams of MV-Diluent in a vial.
- Add 10 drops (medicine dropper) of MV Curing Agent.
- Cap, shake, and refrigerate overnight.
- The mixture should gel in the vial after this procedure to assure a cure in subsequent animal injections.
Catalyzed mixtures will form an elastomeric gel after 90 minutes at room temperature. Curing takes place with non-exothermic cross-linking and minimal volume change.
It has been possible to refrigerate specimens immediately after injection and still obtain complete cure after overnight aging. The procedure decreases odor level for subsequent sectioning.
Perfusion Techniques
Two techniques of tissue clearing are described below. Alcohol-methyl salicylate clearing produces a stiffer tissue, which, from an aesthetic point, provides a pleasing view for gross observation. Glycerin clearing produces a more flexible tissue, allowing easier manipulation for a given vessel.
Alcohol-methyl salicylate clearing
Non-wetting features of MICROFIL® compounds prevent any interaction with blood. Therefore, in the non-surviving animal, a selected vascular bed can be readily perfused without prior washout of blood. Heparinization to maintain blood fluidity, however, has been used to realize improved injection preparations.
For the injection of blood vessels from vascular beds removed post-mortem, washout of clotted blood with saline is advisable.
Selected vascular beds are perfused through their accessible artery and drained through a similar vein. Infusion pressures will vary with the animal’s mean systemic pressure. For organs from the dog, cat, rat, and man, a pressure of 150mm.Hg for arterial filling has been used, and 25 to 50mm.Hg for venous fillings.